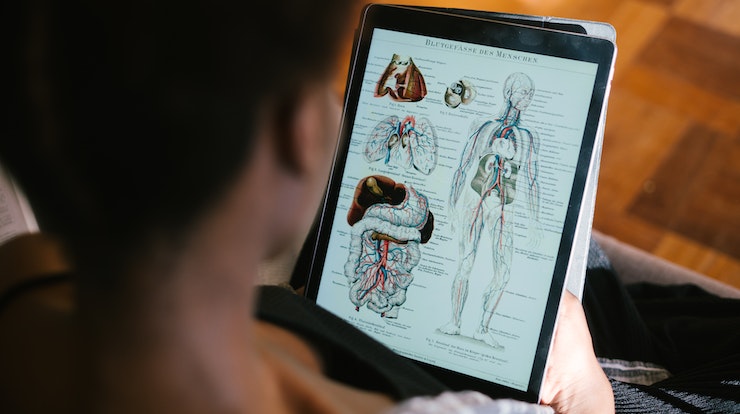
What is Human Anatomy and Physiology? Some important questions
If you are a student or want to generally know about Human Anatomy and Physiology then the first things to know is what are these terms and then some simple questions. These will help you in your further studies as basic knowledge is a must and that is what makes your base strong. So without further ado let’s begin with it.
Before that…
Who should Practice these Human Anatomy and Physiology Questions?
– Anyone wishing to sharpen their knowledge of Human Anatomy and Physiology Subject
– Anyone preparing for an aptitude test in Human Anatomy and Physiology
– Anyone preparing for interviews (campus/off-campus interviews, walk-in interviews, and company interviews)
– Anyone preparing for entrance examinations and other competitive examinations
– All – Experienced, Freshers and Students
What are Human Anatomy and Physiology?
Anatomy is the study of the structure and relationship between body parts. Physiology is the study of the function of body parts and the body as a whole.
What is Blood and its composition?
Blood is a body fluid that flows throughout our body. It mainly consists of plasma but besides that, it also has Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, and Platelets. The main function of blood is to carry oxygen, sugar, and other nutrients to the cells in the body. Blood also carries waste materials from the body cells.
RBC – They carry oxygen to the cells
WBC – They help in fighting the diseases
Platelets – They help in blood clotting
What is Blood Plasma?
Blood plasma is a ‘yellowish liquid’ component of blood that holds the blood cells of whole blood in suspension.
How many chambers are in the Heart?
4 total chambers. left and right atrium. left and right ventricle.
Types of WBC?
Lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils
What are Lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes help in producing antibodies and kill tumor cells.
What is the RBC range in a normal person?
Male – 5.4 million
Female – 4.8 million
What does RBC contain? Where is it made?
RBC consists of hemoglobin. RBC is made in the bone marrow. Their life is up to 120 days, and after that they die.
What are the Different Layers of Heart?
3 layers. Epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
How is Blood Pressure Measured?
Blood pressure is measured with an instrument called a sphygmomanometer. In adults, blood pressure is considered to be normal under a systolic value of 140 mmHg and under a diastolic value of 90 mmHg. Systolic blood pressure is the pressure when the heartbeats, and Diastolic blood pressure is the pressure on the blood vessels when the heart muscle relaxes
What is CSF?
It is actually a clear liquid that is colorless, and it protects our brain and spinal cord from any physical or chemical injuries.
What is Hypothalamus?
It is a part of the brain and it helps in controlling the body temperature and also emotions as it releases various hormones.
What is a Tissue and its function?
Tissues are basically a group of cells that have a similar structure and they perform a similar function. Tissues collectively make up various organs in our body, like the brain and heart.
How many bones does our body have?
206
How many bones does our skull have?
22
Which is the largest gland of the human body?
Liver
How many vertebrae are there in the lumber section?
Five vertebrae in the lumber section.
How many lobes are there in the lungs?
The right lung is divided into 3 lobes & the left lung is divided into two lobes.
What is a nephron?
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidneys.
What is a pupil? What is its function?
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light
to strike the retina.
How many types of photocells are in the retina?
Each retina has about 6 million cones and 120 million rods.
How many bones are present in the middle ear?
3 bones are present in the middle ear. Their names are Incus, Stapes, and Malleus.
What is a bony labyrinth?
The bony labyrinth is a series of cavities in the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
What is transitional epithelium?
It’s present in the urinary system. It is in a relaxed or up-stretched state, transitional epithelium looks like stratified cuboidal epithelium.